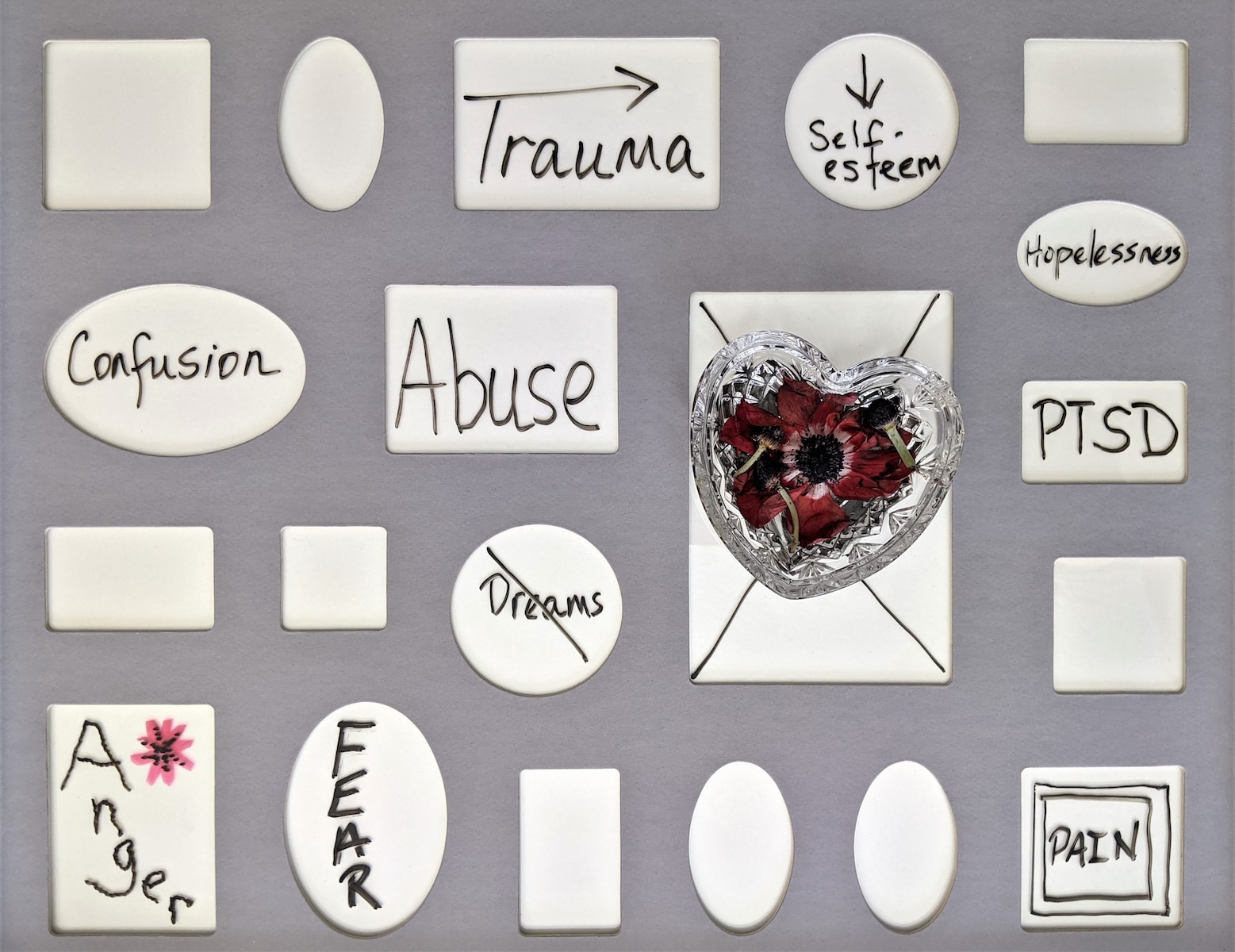
Alcoholism is a complex disease that affects millions of people around the world. It is characterized by a physical and psychological dependence on alcohol, which can lead to negative consequences in many areas of life. While there are several factors that contribute to the development of alcoholism, one that is often overlooked is trauma. Trauma refers to any experience that is emotionally or psychologically distressing, and it can have a profound impact on a person’s mental health and well-being. In this article, we will explore the role of trauma in alcoholism development and discuss ways to heal from the effects of trauma.
The Connection between Trauma and Alcoholism
Traumatic experiences can have a significant impact on a person’s mental health, leading to conditions such as anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). These conditions can be difficult to cope with and can lead to a range of negative coping mechanisms, including substance abuse. In fact, research has shown that trauma is a common underlying factor in addiction, including alcoholism.
Trauma can impact addiction in several ways, including:
- Self-medication: Many people who have experienced trauma turn to drugs or alcohol as a way to cope with the emotional pain and distress they are feeling. Alcohol can provide temporary relief from the symptoms of trauma, such as anxiety and depression, but it ultimately leads to a cycle of addiction.
- Behavioral patterns: Trauma can also impact a person’s behavior, leading to patterns such as impulsivity, risk-taking, and aggression. These patterns can increase the likelihood of substance abuse and addiction.
- Brain chemistry: Trauma can also impact the brain’s reward system, leading to changes in the way the brain processes pleasure and reward. This can lead to a heightened sensitivity to alcohol and other substances, making addiction more likely.
Types of Trauma that Can Lead to Alcoholism
Trauma can take many different forms, and not all traumatic experiences will lead to alcoholism. However, there are several types of trauma that are particularly likely to contribute to addiction, including:
- Childhood trauma: Traumatic experiences during childhood, such as physical or sexual abuse, neglect, or exposure to violence, can have a profound impact on a person’s mental health and well-being. These experiences can lead to a range of negative coping mechanisms, including substance abuse.
- Combat trauma: Trauma experienced during military service, such as exposure to combat, can also contribute to addiction. Many veterans turn to alcohol as a way to cope with the emotional pain and distress of their experiences.
- Sexual trauma: Sexual trauma, such as rape or sexual assault, can have a lasting impact on a person’s mental health. Many survivors turn to alcohol as a way to cope with the emotional pain and distress of their experiences.
Healing from Trauma and Alcoholism
Healing from the effects of trauma and addiction can be a long and difficult process, but it is possible. The first step is to seek help from a mental health professional who specializes in trauma and addiction. A therapist can help you work through the underlying issues that are contributing to your addiction and provide you with the tools and support you need to heal.
There are also several self-care practices that can be helpful in healing from trauma and addiction, including:
- Mindfulness practices: Mindfulness practices such as meditation and yoga can help you develop a greater sense of awareness and self-compassion, which can be helpful in managing the symptoms of trauma and addiction.
- Exercise: Regular exercise can be a powerful tool in managing the symptoms of trauma and addiction. Exercise can help you release pent-up emotions, reduce stress, and improve your overall physical and mental health.
- Healthy coping mechanisms: Finding healthy coping mechanisms, such as journaling, painting, or spending time in nature, can be a helpful way to manage the symptoms of trauma and addiction without turning to substances.
- Support groups: Joining a support group, such as Alcoholics Anonymous or a trauma survivors group, can provide you with a sense of community and support as you work through the healing process.
FAQs about Trauma and Alcoholism
Is trauma always a factor in alcoholism development?
No, trauma is not always a factor in alcoholism development. There are many different factors that can contribute to addiction, including genetic, environmental, and social factors.
Can alcoholism cause trauma?
Yes, alcoholism can cause trauma, particularly if it leads to negative consequences such as legal problems, relationship issues, or health problems.
Can trauma be healed?
Yes, trauma can be healed with the right support and treatment. While the effects of trauma may never fully go away, it is possible to learn to manage the symptoms and live a fulfilling life.
What is the best treatment for trauma and alcoholism?
The best treatment for trauma and alcoholism will vary depending on the individual’s needs and circumstances. A combination of therapy, medication, and self-care practices may be helpful in managing the symptoms of trauma and addiction.
Trauma can play a significant role in the development of alcoholism, and it is important to address the underlying issues in order to achieve lasting recovery. If you or someone you love is struggling with addiction and trauma, it is important to seek help from a mental health professional who specializes in these issues. With the right support and treatment, it is possible to heal from the effects of trauma and addiction and live a fulfilling life. Remember, healing is a journey, and it is never too late to start.